Today, books and painters have closer relations than before. But, in the times of middle age when no one knew what’s the position of earth in the universe, people used to have books made with gold and jewel or the books listing mythological beasts and also believing those beasts to be real. There also happened to be the world’s first art-history book written in 16th century. Read further, to see how artists used their art beyond the regular oil and canvas.
1. Bestiary
Bestiary is a compliment of the different animals and beasts with detailed description as well as with a fine illustration of the beast with some moral message at the end.
It could have totally imaginary animals from myths, folklore and fairy-tales (Unicorn, Centaurs) or could have the regular animals (tiger, goose, bear) with mythical stories and beliefs attached to them. There could also be a fusion of existing animals (Basilisk, ant-lion) creating a deformed beast.
These Bestiaries were popular back in time for its graphically rich depiction, detailed descriptions and mainly because of the unimaginable animals listed in them. Most of the people considered those animals being real.
The figures and illustrations in Bestiaries were depicted by painters. But, painters also used to create their own Bestiaries.
Leonardo da Vinci kept his personal Bestiary. In it, apart from many beasts, he has explained why he put an ermine in his groundbreaking art work, Lady with an Ermine.
2. The Lives by Giorgio Vasari
Popularly known just as The Lives or Vite was originally entitled as Le Vite De’ Più Eccellenti Pittori, Scultori, E Architettori Da Cimabue Insino A’ Tempi Nostril meaning Lives of the Most Excellent Italian Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, from Cimabue to Our Times.
It is called as “the first important book on Art History”. Before Giorgio Vasari, no other artist or art historian tried to compile the lives of the important artists in one book. Thus, this is the first book providing first-hand information about the well-known artists ranging from 13th Century to the renaissance period.
The fact that Giorgio Vasari wrote this book while the artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo were living makes the book a first-hand information for such renaissance artists.
Read here, for the detailed information about Vasari’s life and his work of The Lives.
3. Illuminated Manuscript
Illuminated Manuscripts were excessively used in the middle ages, where wealthy people used to have custom-made books with excessive decoration with gold and silver leaves. Pages would be excessively decorated with designs and figures, leaving very little space for the texts.
The fonts used in the majority of the illuminated Manuscripts (and many other middle age books) were called Blacklatter or Gothic Script. They were famous between the time periods of 11th century to 17th century.
So, any book from middle ages with excessive decorations using gold, silver and designs and little space for text on each page is called Illuminated Manuscripts. In today’s market of antique things, such books worth quite a price as every book was custom made and thus, unique from each other. Not to mention, that the decorative designs from the Middle Ages are sometime considered priceless. There were also specialists available for such work. The most known Illuminated Manuscripts artists were the Limbourg brothers (1385-1416).
Rich people in the middle age used to have such expensive Illuminated Manuscripts.
4. Codex Leicester
Codex Leicester is Leonardo da Vinci’s most famous scientific writing purchased by Bill Gates in 1994 for around $ 30 million. This scientific journal of Leonardo among total of 30 is considered one of the most important. It consists the theories and derived facts from observations. Some of them were astonishingly accurate to the real facts (without having any advanced technology) while few were partially wrong.
The main subject of this scientific codex by Leonardo is the observations of water’s movement and its reaction when it collides with any object. There were also studies of moon, mountains, tectonic plates and fossils described in it.
Leonardo wrote the full codex in Italian, his native language, with his habit of mirror-writing (he was afraid that someone will copy his research). Obviously, Leonardo’s various detailed studies about everything were delivered in his arts inescapably. You can read the full codex Leicester online here.
5. De Divina Proportione
De Divina Proportione was a mathematical book published in 1509 written by Luca Pacioli and illustrated by Leonardo da Vinci. Writer was an expert mathematician. Leonardo’s contribution in the book were the drawings included in the book. According to Luca Pacioli’s instructions Leonardo drew the mathematical proportions and designs. He also learned some mathematics from the writer as well improving his own knowledge.
It is possible that Leonardo learned about the Golden Ration or the Devine Proportion from him and applied in his famous studies like Vitruvian man. The following image is a part of De Divina Proportione which was only depicted by Leonardo da Vinci.
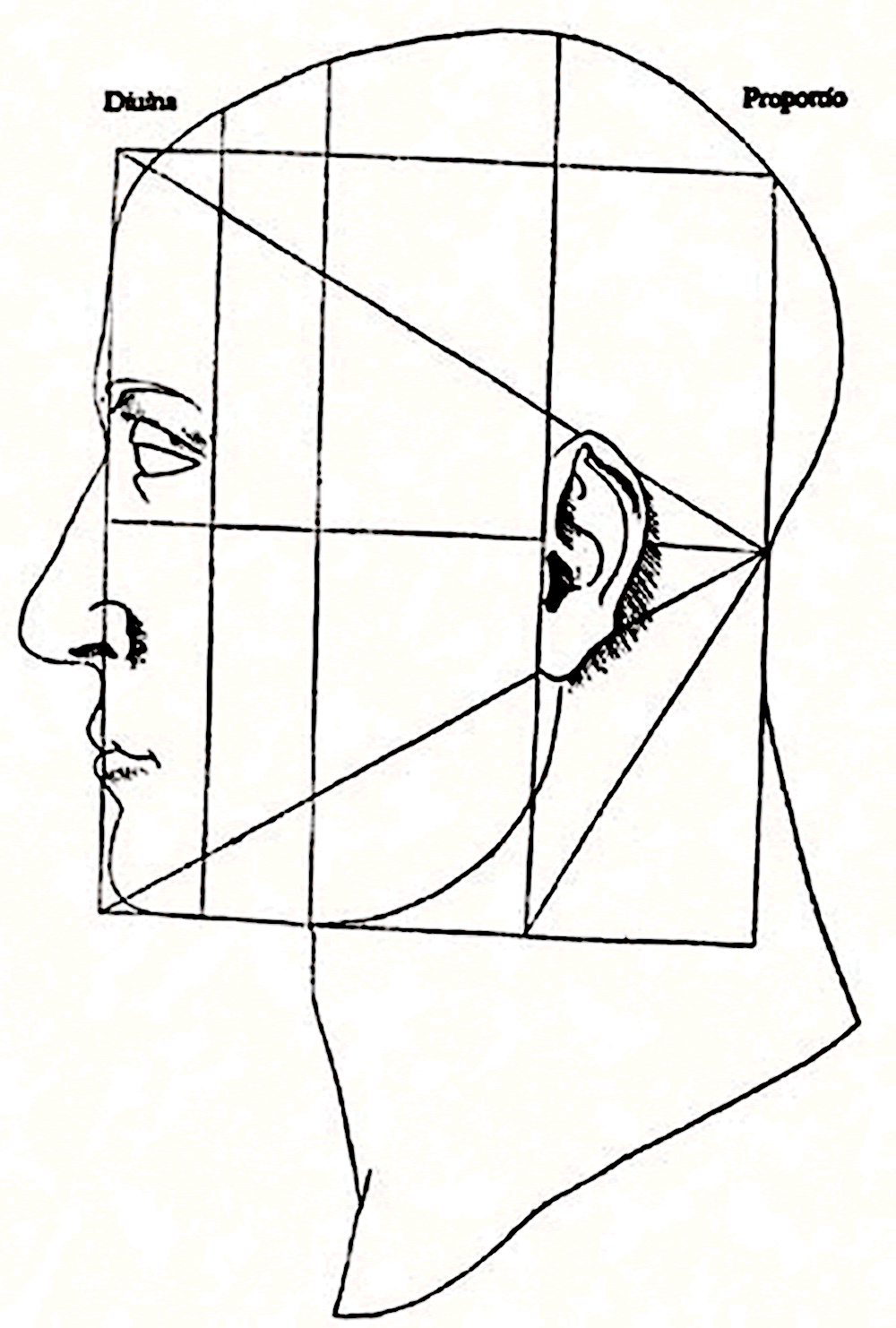
Divine Proportion – Golden ration in Human Face by drawn Leonardo da Vinci
6. Akbarnama
Akbarnama was a two-part illustrated book depicting the anecdotes of the life of the Indian Mughal Emperor Akbar from 16th century. The name literally translates as the Book of Akbar.
Many Indian artists contributed in the Akbarnama. Though, the prominent artist was the Indian miniature painter Basawan. The book was a break-through for Indian Art and a push forward for the contemporary artists who got the admired and encouraged under Akbar’s reign.
7. Book of Hours
Book of Hours were the religious books consisting of prayers, psalms and writings hugely popular in middle ages. People used to have them in their pockets during the daytime and according to the church’s decree, they needed to pray every after some hours, multiple times in a day. These books came handy for whom who couldn’t remember all the prayers or religious psalms.
Though, the rich people used to have them decorated with gold, silver and other excessive decorations. Thus, Book of Hours is basically a Illuminated Manuscripts. But, their huge popularity in the middle age puts it on the list. Most of the illuminated Manuscripts found today are Books of Hours. Their layout were similar to other Illuminated manuscripts with similar fonts, designs, use of gold and silver and the miniature paintings included on each page.
 8. Emblem Books
8. Emblem Books
Emblem books were the printed books with a print and some text regarding to the painting. Each combination of the picture and text in the book was destined to deliver some message, knowledge or moral instructions to the reader. They were popular in 16th and 17th century in Europe.
Over the time, the Emblem books got popular and many big artists started to produce such books. Otto van Veen, the teacher of Peter Paul Rubens was a noted artist to produce magnificent Emblem books.






